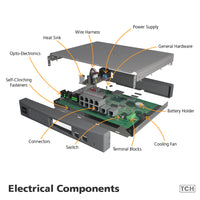
TCH sources electro-mechanical components from an extensive network of key vendors. While these components have various uses, our customers' applications are usually for IOT Controls, Building System Management, Security, Healthcare, Aviation, HVAC, Telecommunications, Data communications, and more.
Our exclusive vendors:
Explore our 30+ vendors in the navigation for more information. We're working hard to have electronic components available online. For any product inquires or questions, please contact us.
Electronic Components
Power Supply
Sometimes confused with a power source, the source is the root of the incoming electricity while the power supply converts the source into a suitable format and voltage. There are various choices available depending on what requirements are needed. A power supply consists of the following elements: transformer, rectifier, filter, and regulator circuits. It generates notable heat, which requires a type of thermal management, such as heat sinks.
Heat Sink
Heat sinks are one of the most popular forms of thermal management for electronic equipment. It's a component that dissipates the heat flow away from the device. This allows the source to operate at cooler temperatures causing less strain and prolonging its life. Depending on the amount of heat generated, small amounts can use a simple heat sink, while more complicated ones are needed for significant heat.
Calculations are needed to know the required performance for a heat sink. The simplest equation to determine this is:
Thermal resistance of the heatsink = Max temperature rise / watts dissipated
There are also calculators online to assist with calculations.
Cooling Fan
Cooling fans draw lower temperature air from the outside while expelling the heat from within towards a heat sink to cool the device and components. There are several air moving devices such as fans (axial, propeller, and tubeaxial) and impellers or blowers (centrifugal and crossflow). After choosing the right type of fan/blower for your application, calculate the airflow (measured in CFM) to distinguish the fan's best size and shape.
A crucial factor to consider is how much heat dissipation is necessary. Calculated with the following equation:
Q = mCpDT
Where:
Q = Amount heat transferred to the system, in WattsCp (the specific heat of air, J/kg x K)
m = Mass flow rate of air, kg/s
DT = Desired Air Temperature Differential, K
We must consider the relationship between mass flow rate and volumetric flowrate:
m = rG
Where:
G = Volumetric Flow Rate, m3/s
r = Air Density, kg/m3
The following equation calculates Volumetric Flow Rate:
G = Q / (rCpDT)
By utilizing this formula, you can estimate the airflow required to obtain the desired air temperature in DT.
The actual operating airflow required is found by the point of intersection of the fan vs. system resistance curve.
Battery Holder
Battery holders safely secure cells in place while sending power from the batteries to the device. Often built into the electrical equipment, battery holders are also purchasable as an external attachment. When choosing a holder, consider the following:
- Battery size
- Compatibility
- Mounting method
- Design and shape
- Manufacturer and quality
Terminal Blocks
Also known as connection terminals or terminal connectors, terminal blocks are electrical-mechanical devices used to connect wires to wires, wire to board, or wire to devices. Types of terminal blocks:
- Printed circuit board
- Panel mount barrier blocks
- PCB barrier blocks
- Panel mount euro strips
- Din rail terminal blocks
While each type of block can be used in different applications, they all safely connect electrical components. Although connecting two wires without a terminal block is possible, more than that can be difficult and dangerous.
Switch
A switch is an electromechanical component that allows for making, breaking, or changing the electrical current. Since switches are used widely in various applications, there are many types available:
- Toggle switch
- Push-button switch
- Rocker switch
- Rotary switch
- Slider switch
- DIP switch
- Tactile switch
- Proximity Switch
- Snap switch
Self-Clinching Fasteners
Self-clinching fasteners are a useful and cost-efficient method to attach components without welding. They can be threaded or non-threaded and are pressed permanently into sheet metal. Some common styles are studs, nuts, and spacers, but there is a multitude of options. Benefits of using self-clinching fasteners over standard fasteners are:
- Fewer components needed for assembly
- Reduced assembly time and costs
- Can withstand heavy torque loads
- More durable
Connectors
When connecting circuits, connectors are often used since they provide a method to form removable connections and a continuous electrical current path. Connectors have male-ends and female-ends that can connect either permanently or, more often, temporarily. They help reduce time and labor when assembling and installing electrical devices.
Wire Harness
A wire harness is a group of wires gathered to transmit power and signals to an electronic device. They are a safe and cost-efficient electrical solution to help improve organization.